PART 1

The purpose of this 3 part report: Alopecia (hair loss) happens to everyone, to one degree or another, at some point in life. I'm offering this information so that if it’s already happening to you, or if it begins to happen in the future, you'll have everything you need to know at your finger tips and can take action without having to do weeks and weeks of research.
What you’ll learn in this 3 part report: Part 1
What is the cycle of hair growth? What is Alopecia? What types of Alopecia are there? What are the symptoms of Alopecia? What causes Alopecia? What types of Alopecia can be reversed?
Part 2 What are Human Growth Factors (HGFs)?
What can Human Growth Factors do for you?
Part 3 What types of Alopecia treatments are available? What roll does Hormone Replacement Therapy play in reversing alopecia? What roll does vitamin supplementation play in reversing alopecia?
How can Human Growth Factors help reverse Alopecia?
How can Micro Derma Rolling help reverse Alopecia? What treatments actually work to reverse Alopecia?
What treatments take 3-12 months to see new hair growth? What treatment takes 2-3 weeks to see new growth?

THE SECRET LIFE OF HAIR
Each hair on your head has its own individual life cycle. A strand grows for up to 6 years (anagen phase). Then it starts to die (catagen phase), and after about 6 weeks falls out. Then the hair follicle (root sac) rests for around 6 months (telogen phase) before a new hair starts growing to replace it. This whole process is controlled by what’s called Human Growth Factors (HGFs), chemicals that the body produces and distributes via the blood stream.
As we age this cycle becomes shorter and the hair doesn’t grow back as fast, doesn’t grow as long, becomes thinner, and loses it’s color. The main reason for this is atrophy (shrinkage) of the blood supply to each hair follicle (root sac), and the thinning of the scalp itself. Although there are several reasons for Alopeica (hair loss) which you will find out about in Part 2 of this report, one of the main reasons for this ‘atrophy’ is the decline of, or lack of, hormones in both male and female, estrogen and progesterone in females and testosterone and progesterone in males. Replacing these hormones is vital to the health and overall longevity of the whole body, but it's vital to hair growth or regrowth.
WHAT IS ALOPECIA?
Alopeica definition: the partial or complete absence of hair from areas of the body where it normally grows; baldness. Doctors use 'alopecia' to refer to various forms of hair loss, including Alopecia Areata, a sudden loss of hair in patches that involves little or no inflammation.

WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF ALOPECIA?
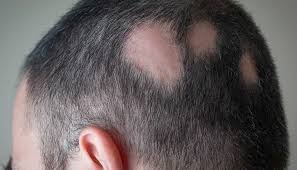
Alopecia Areata (patchy) Is said to be an autoimmune condition that starts with hair falling out in patches, usually in one or more round or oval patches on the scalp and/or body including; the eyelashes, eyebrows, beard, body hair, and pubic hair.
In Alopecia Areata, cells from the immune system gather around the hair follicles (root sacs) and stop them from producing another hair.
The first symptom of Alopecia Areata is often sudden, patchy hair loss, which can grow larger. In some cases, hair can fall out so fast that all the scalp hair is lost without any patches appearing.
Many people do not experience pain or other symptoms from Alopecia Areata. However, in some people, hair loss can be accompanied by tingling, itching, burning, headaches or even pain in the skin.
Types of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia Areata can sometimes develop into either Alopecia Totalis (hair loss over the whole scalp) or Alopecia Universalis (hair loss over the whole body), but mostly it is patchy and eventually grows back. IN some cases, the patchy hair loss happens over time, and never develops into Alopecia Totalis or Alopecia Universalis: this is known as Persistent Patchy Alopecia Areata, or, Chronic Alopecia Areata.
Diffuse Alopecia Areata is the sudden thinning of the hair all over the head rather than patches. This type of Alopecia is also called Alopecia Areata Incognita. This type of Alopecia looks very similar to Telogen Effluvium and Androgenetic Alopecia which makes it more difficult to diagnose.

Telogen effluvium (definitions of effluvium. a foul-smelling outflow or vapor (especially a gaseous waste) type of: discharge, emission. a substance that is emittd or released). Is the thinning or shedding of hair resulting from entering the telogen phase (the resting phase of the hair follicle) too early. It’s in the telogen phase of hair growth that hairs can begin to shed too fast, where usually we lose about 125 hairs a day, with this type of alopecia daily the loss can be much more substantial.

Androgenetic Alopecia (male or female pattern hair loss) Even though the baldness for men and women differ, they both have a common cause.
In men, hair loss typically happens on the top and front of the head. In women, thinning and baldness, usually occurs on the top and crown of the head. This type of thinning in women mainly starts as a widening of the center part and does not affect the front of the hair.

Alopecia Totalis Alopecia Totalis is the total loss of all scalp hair. In some people, the hair falls out very rapidly that it never even goes through the Alopecia Areata (patchy) stage.

Alopecia Universalis Alopecia Universalis is hair loss across the entire head, face (including eyebrows and eyelashes), and the rest of the body (including pubic hair). Note, many people experience forms of Alopecia Areata that are somewhere between Alopecia Totalis and Alopecia Universalis, so can lose some but not all body hair, or some but not all facial hair.

Alopecia Areata Ophiasis Is where hair falls out from the sides and lower back of the scalp. Alopecia Areata Ophiasis can be harder to treat because it does not respond as quickly to medications or hair regrowth products. There is another form of alopecia areata, called alopecia areata sisaipho, in this form hair is lost from the front of the scalp and forehead, and sometimes the eyebrows.

Alopecia Barbae Is hair loss of the beard and moustache. Alopecia Barbae usually only happens in the beard area, but it can also happen along with hair loss of the scalp. Alopecia Barbae causes the beard hair to fall out in round or oval patches. Sometimes the hair at the edge of the patches turns white.

Does the Condition Affect Anything Other Than Hair?
Between 10–50% of people with Alopecia Areata also experience nail changes like pitting and ridges.
This is the end of Part 1 of this report. If you're experiencing hair loss of any kind I hope this information has shed some light into its cause.
Thank you for your time, Sindi Holmlund
.png)